Which Best Describes the Chemical Behavior of Amines
The method one can describe the fluid-phase behavior of mixtures of molecules compris- ing those groups over broad ranges of temperat ure pressure and composition. Amines are molecules that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds.
Amines are compounds that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair of electrons.

. In case of replacing two out of three hydrogen atoms we get secondary amine and when all the three hydrogen atoms are replaced tertiary amines are formed. H 2 N-CH 2-NH 2. Also write chemical equations of the reaction involved.
An -OH group has replaced an H atom on the ring. Amines are extremely interesting chemical substances due to their strong electron donating capability. They are the derivatives of ammonia wherein one or more hydrogen atom can be replaced by substituent groups such as alkyl or aryl.
Amines which are merely organic derivatives of ammonia are also tetrahedrally hybridized and are comparably basic and nucleophilic to ammonia. Considering the wide range. Application of amines are quite variety such as to make medicines azo-dyes anticorrosion agents drugs agrochemicals or most specifically diethylamine is principally used as a production of vulcanization accelerators.
Amines are derivatives of ammonia where is one or more hydrogen atoms replaced by a. The additional nitrogen substituents in 2º and 3º-amines are designated by the prefix N-before the group. According to the current technological progress chemical absorption with amines is mostly used for capturing CO 2 due to its high CO 2 absorption rate and capacity and mild operating conditions compared with physical adsorption and membrane separation.
Various nomenclatures are used to derive names for amines but all involve the class-identifying suffix ine as illustrated here for a few simple examples. Cyclopentene H2O yields 1hydroxycyclopentane a. A number of aqueous solutions of amines are studied incl uding linear branched aliphatic and cyclic amines.
Amines are classified into four categories namely primary secondary tertiary and cyclic. New Kinetic Model That Describes the Reversible Adsorption and Desorption Behavior of CO2 in a. These are classified on the basis of the presence of replaceable hydrogen atoms.
Amines are basic in nature and in most of the reactions they act as nucleophiles. The hydrophobic hydrocarbon tail. The best model consisted of three parallel reactions which was consistent with PEI having three different amine sites.
Describe a method for the identification of primary secondary and tertiary amines. For 1º-amines such as butanamine first example this is analogous to IUPAC alcohol nomenclature -ol suffix. Hence chemical behavior of amines is similar to ammonia.
Amines are basic in nature and in most of the reactions they act as nucleophiles. Amines are organic compounds and functional groups which contain a nitrogen atom with a lone pair of electrons. Similarly when all the three hydrogen atoms are replaced tertiary amines are formed.
The basicity of amines is often discussed indirectly in terms of the acidity of their respective conjugate acids. Amines but not amides exhibit basic behavior c. Amines react with aqueous solution of acids to form salts.
An -OH group has been added to the reactant. Salts of amine are typical ionic solids. What class of compounds is primarily responsible for the pleasant smell of many fruits.
The study of design and operation of these. An organic compound with multiple amine groups is called a diamine triamine tetraamine and so forth based on the number of amine groups also called amino groups attached to the molecule. When you can replace two out of three hydrogen atoms we get secondary amine.
CH₃-CH₂-CH₂-NH₂ H₂O l CH₃-CH₂-CH₂-NH₃ aq OH aq. These reactions support the basic nature of amines. The nitrogen atom in an amine has a lone pair of electrons and three bonds to other atoms either carbon or hydrogen.
An H atom and an -OH group have been added to the reactant. When one of the three hydrogen atoms is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group the amine is primary. A chemical substance that is released at the end of a nerve travels across the synaptic gap between the nerve and another nerve and then bonds to a receptor site on the other nerve triggering a nerve impulse.
Salts of amine are typical ionic solids. The chemical formula for methylene diamine also called diaminomethane for example would be as follows. You might recall that amines are completely neutralized protonated by carboxylic acids.
Amine group -NH₂ has neutral charge bet when accepts one proton H has positive charge. Benzenesulphonyl chloride C 6 H 5 SO 2 Cl which is also known as Hinsbergs reagent reacts with primary and secondary amines to form sulphonamides and tertiary amine does. What part of the soap molecule is oriented on the inside of the micelle.
Which of the following best describes the changes that occurred in the reaction below. A primary amine is one when you can replace one of the three hydrogen atoms by an alkyl or aryl group. The Chemical Abstract Service has adopted a nomenclature system in which the suffix -amine is attached to the root alkyl name.
Only secondary or tertiary amines can be cyclic. What best describes the chemical behavior of amines. Amides do not exhibit basic behavior b.
Both amines and amides exhibit basic. The SAFT family of EOSs is well known for its suitability to model complex mixtures of associating fluids and has been used in a number of studies. Hence chemical behavior of amines is similar to ammonia.
These reactions hold the fundamental nature of amines. Soap molecules from micells when dissolved in water. Amines react with aqueous solution of acids to form salts.

Solved 6 What Class Of Compounds Is Represented By The Chegg Com
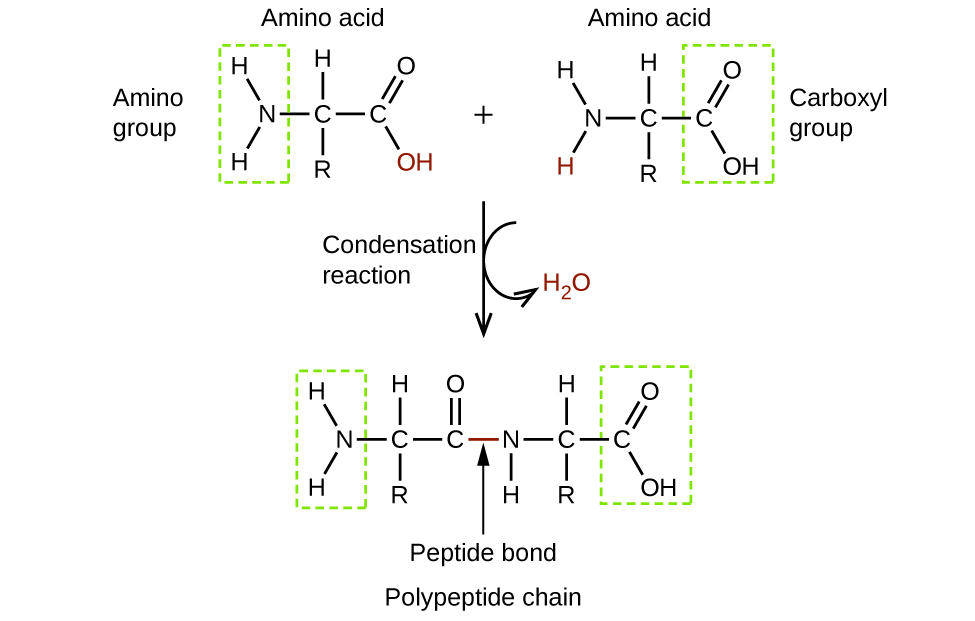
20 4 Amines And Amides Chemistry
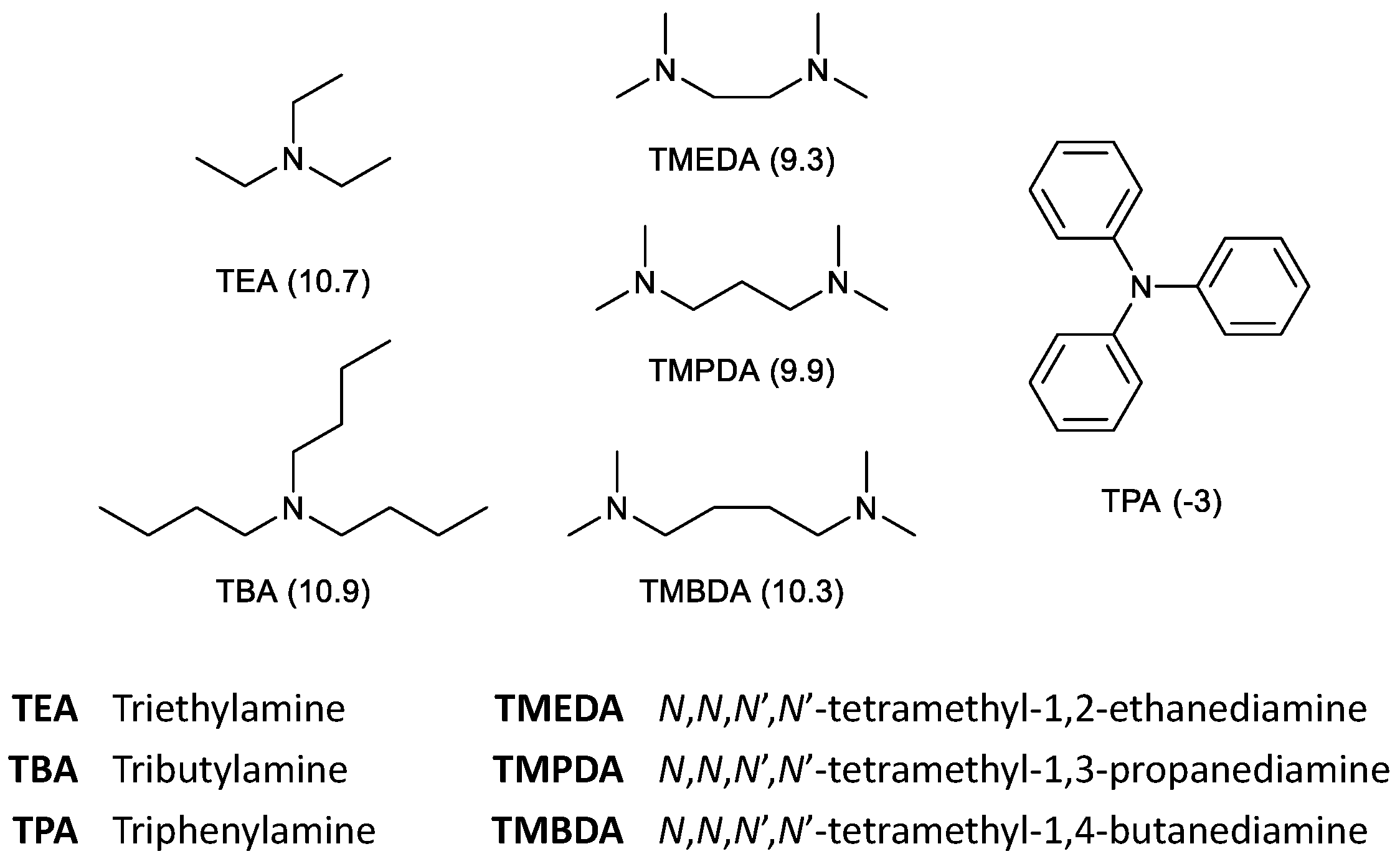
Molecules Free Full Text Reductive Hydroformylation Of Isosorbide Diallyl Ether Html

A General Maillard Reaction Between Lactose And An Amine Download Scientific Diagram
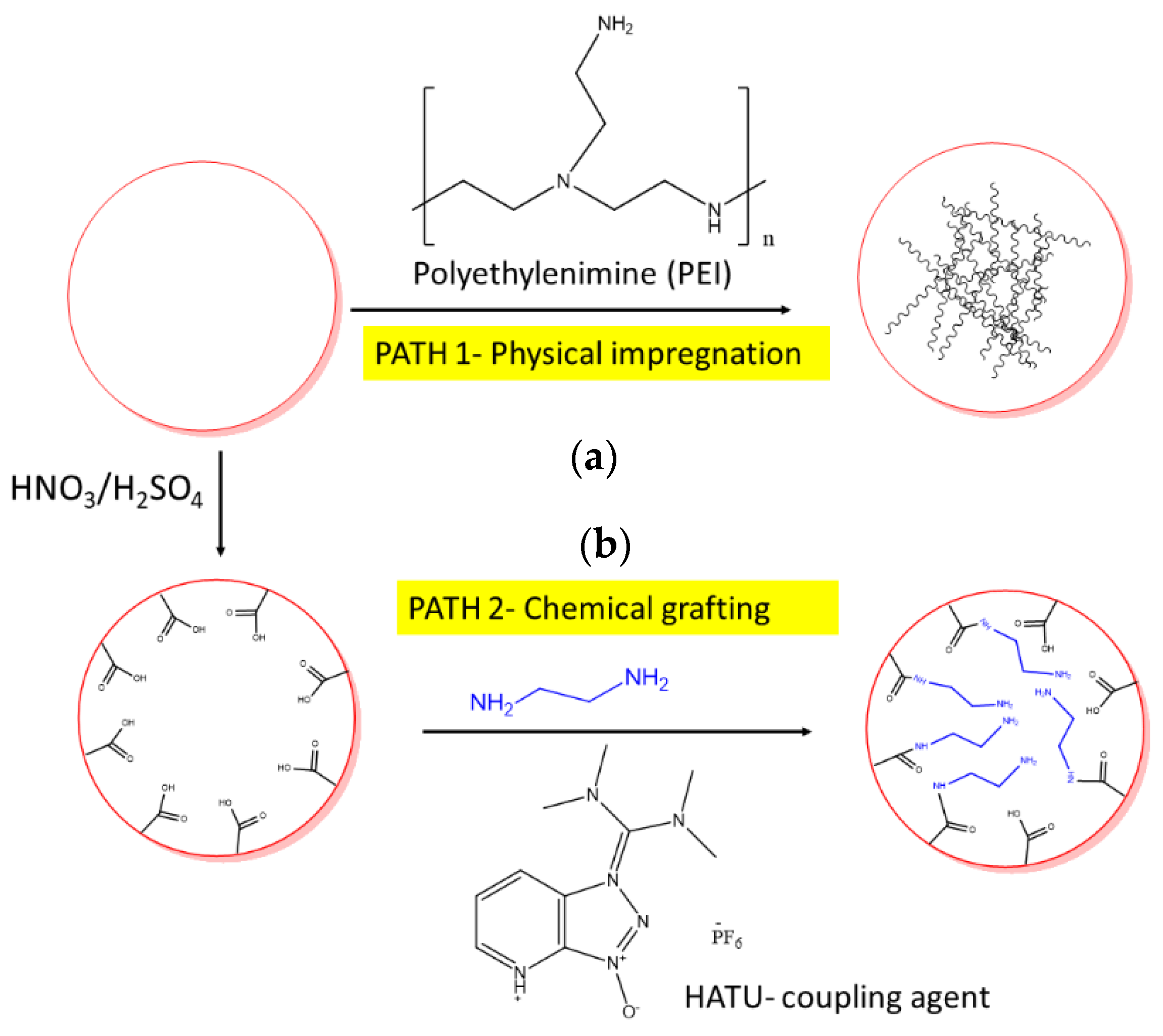
Atmosphere Free Full Text Carbon Dioxide Capture Through Physical And Chemical Adsorption Using Porous Carbon Materials A Review Html
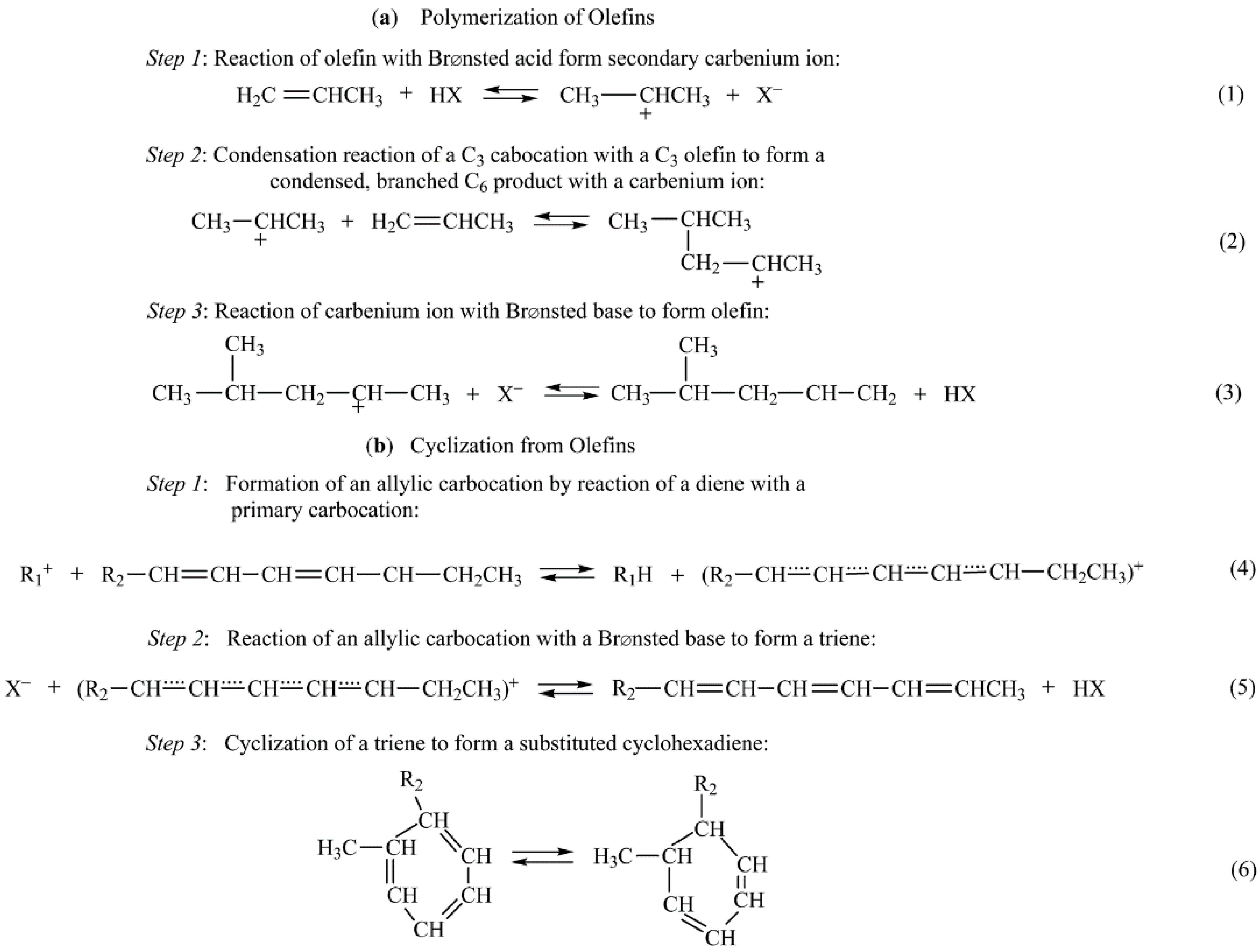
Catalysts Free Full Text Heterogeneous Catalyst Deactivation And Regeneration A Review Html

A General Maillard Reaction Between Lactose And An Amine Download Scientific Diagram

9 15 Done Organic Chemistry Midterm Fillab 1 The Chegg Com

Solved 6 What Class Of Compounds Is Represented By The Chegg Com
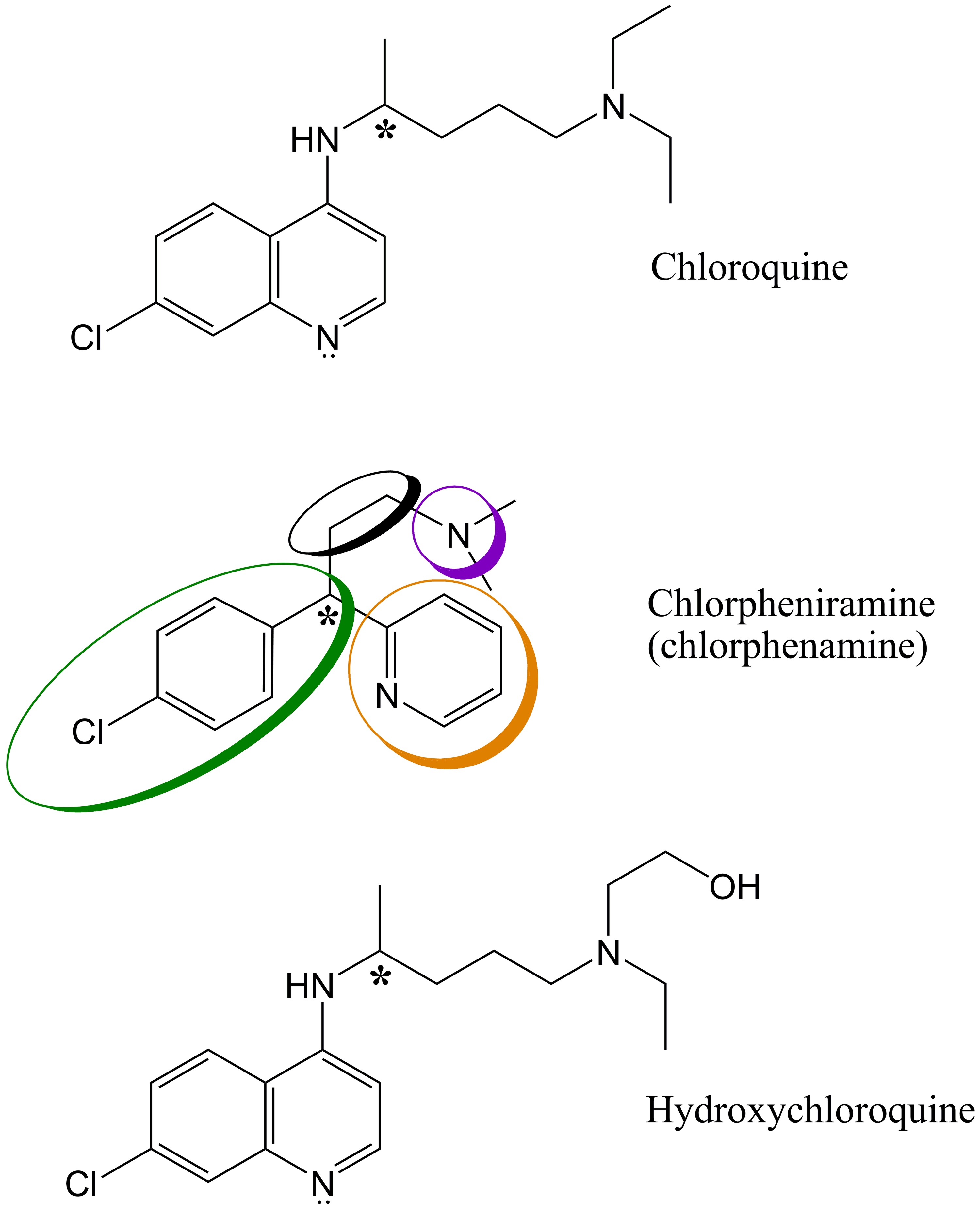
Cureus Molecular Modeling And Preliminary Clinical Data Suggesting Antiviral Activity For Chlorpheniramine Chlorphenamine Against Covid 19

15 Questions And Answers Chemistry Uos Studocu

Synthesis Of P Functional Molecules Through Oxidation Of Aromatic Amines Hiroto 2019 Chemistry 8211 An Asian Journal Wiley Online Library

Pdf Cure Behavior And Kinetic Study Of Diglycidyl Ether Of Bisphenol A With A Tertiary Amine Salt By Differential Scanning Calorimetry

A General Maillard Reaction Between Lactose And An Amine Download Scientific Diagram
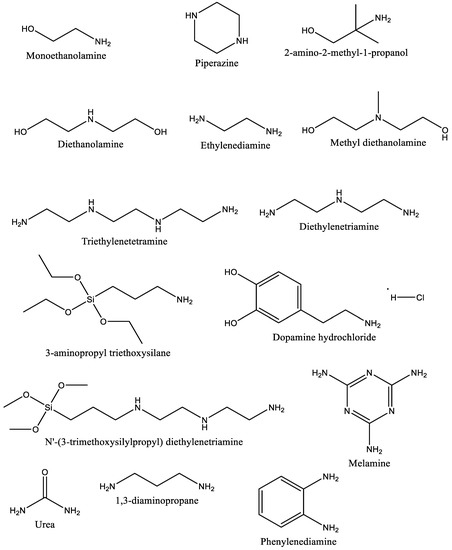
Atmosphere Free Full Text Carbon Dioxide Capture Through Physical And Chemical Adsorption Using Porous Carbon Materials A Review Html
Pdf Effects Of Ruthenium Hydride Species On Primary Amine Synthesis By Direct Amination Of Alcohols Over A Heterogeneous Ru Catalyst



Comments
Post a Comment